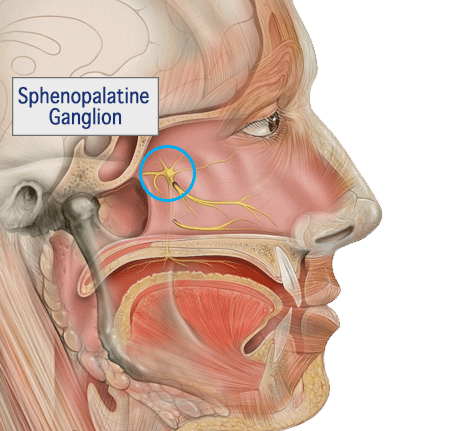
The Sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) is a cluster of nerve cells located under the tissue lining the back of the nose. This bundle contains autonomic nerves specialized in organ function and sensation. By applying a local anesthetic to the nerve bundle, nerve impulses may be blocked thus stopping the transmission of pain. This is otherwise known as an SPG Block. This is through the nose and is the least invasive way to access the SPG— and the medication used is a local anesthetic such as lidocaine (the same or similar medication that is injected by a dentist or used to anesthetize a laceration before stitches). We can do this without a needle because the outer tissue linings are only millimeters thick and absorb the medications well.
Why is this a novel way for treating migraines? The SPG has connections to the brainstem (where cluster and migraine attacks may be generated) and to the meninges (coverings of the brain) by the trigeminal nerve (through the ophthalmic branch). Pain receptors are activated when the blood vessels become dilated and inflamed. Pain impulses are then transmitted through the trigeminal nerve, eventually to the sensory areas of the brain, and are perceived as pain. In migraine and cluster headache, nerves carrying these pain signals pass through the SPG, with some making connections to the autonomic nerves - this is why some headaches can trigger blurry vision, tearing of the eyes, facial droop or runny nose.
Normally, there are no serious side effects associated with the treatment. Common reactions may include eye watering, a feeling of tightness in the face, numbness in the throat.
SPG is highly effective at providing pain relief but also useful in migraine prevention and maintenance with routine blocks. We have special pricing for bundled treatments.